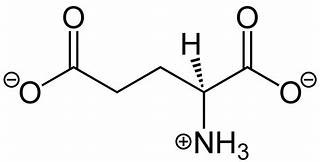
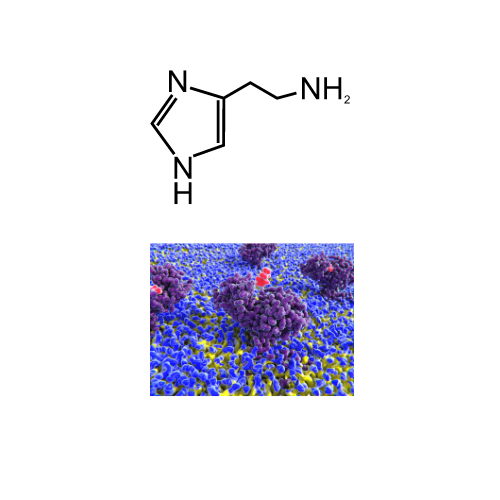
Neurotransmitters are the brain’s chemical messengers, playing a pivotal role in regulating mood, energy levels, appetite, sleep, and more. An imbalance in these crucial chemicals can lead to a variety of health issues, from depression and anxiety to sleep disorders and cognitive impairments. Understanding neurotransmitters and how to maintain their balance is essential for overall well-being.
What Are Neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are produced within the brain and are responsible for transmitting signals across the synapse, the gap between neurons. They bind to specific receptors on the surface of target cells, much like a key fits into a lock, initiating various physiological responses.
Executive function mechanisms involve several neurotransmitters that play critical roles in higher-order cognitive processes.
Let’s explore some of these key neurotransmitters:
Acetylcholine (ACh): Widely distributed throughout the nervous system, ACh is essential for memory, attention, and learning. Dysfunction in the cholinergic system can impact executive functions.
Here are some strategies to support and enhance your cholinergic system:
Choline-Rich Diet:
Choline is a precursor for acetylcholine. Include foods rich in choline, such as egg yolks, soy, liver, and seeds of vegetables and legumes. These provide the necessary nutrients for acetylcholine synthesis.
Supplement with Choline:
Choline supplements can directly increase acetylcholine levels. Choline is an essential nutrient that cannot be synthesized by the body, so supplementation is beneficial.
Physical Activity:
Regular exercise positively influences neurotransmitter levels, including acetylcholine. Aim for both aerobic and strength training exercises.
Stress Management:
Chronic stress negatively impacts the cholinergic system. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga.
Ensure Adequate Sleep:
Quality sleep supports neurotransmitter balance, including acetylcholine. Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and create a restful environment.
Dopamine (DA): Known for its role in reward, motivation, and pleasure, DA also influences executive functions such as decision-making, planning, and working memory. The prefrontal cortex, where executive functions reside, is rich in dopamine receptors.
Balancing your dopamine system, which is closely tied to executive functions, can significantly impact your cognitive performance.
Here are some strategies to achieve that balance:
Nutrition and Precursors:
Tyrosine: Consume foods rich in tyrosine, an amino acid that serves as a precursor for dopamine synthesis. Examples include lean meats, dairy products, soy, and nuts.
Protein-Rich Diet: Protein provides the necessary building blocks for neurotransmitter production, including dopamine.
Physical Activity:
Regular exercise positively influences dopamine levels. Both aerobic and strength training activities can enhance dopamine release.
Stress Management:
Chronic stress negatively impacts dopamine function. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
Sleep Optimisation:
Prioritize quality sleep. During deep sleep, the brain restores neurotransmitter levels, including dopamine.
Avoid Excessive Stimulants:
While caffeine can temporarily boost dopamine, excessive consumption can lead to tolerance and imbalance. Moderation is key.
Mindfulness and Reward Anticipation:
Engage in activities that promote mindfulness and reward anticipation. Dopamine is released when the brain anticipates a reward. Cultivate a positive mindset and celebrate small achievements.
Supplements and Lifestyle Choices:
Consider supplements like L-tyrosine or Rhodiola rosea (an adaptogen) to support dopamine production.
Cold Showers: Cold exposure may enhance dopamine receptor sensitivity.
Norepinephrine (NE): NE, also called noradrenaline, contributes to alertness, attention, and vigilance. It modulates executive functions by enhancing cognitive flexibility and response inhibition.
Balancing norepinephrine levels is essential for maintaining optimal cognitive function, especially when it comes to executive functions. Here are some natural strategies to achieve that balance:
Stress Management:
Reduce emotional and physical stress in your daily life. Chronic stress can lead to excessive norepinephrine release. Engage in activities like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to promote relaxation and balance.
Adequate Sleep:
Prioritise quality sleep. Lack of sleep can disrupt neurotransmitter balance, including norepinephrine. Aim for seven to nine hours of restful sleep per night.
Regular Exercise:
Physical activity helps regulate neurotransmitters. Aim for at least 30 minutes a day, at least five days a week. Exercise promotes overall well-being and supports norepinephrine balance.
Dietary Choices:
Include foods rich in meats, chicken, fish, nuts, eggs, and cheese. These provide nutrients that support norepinephrine synthesis.
Glutamate: As the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, glutamate is crucial for synaptic plasticity and learning. It affects executive functions by shaping neural networks and facilitating information processing.
Balancing glutamate levels is crucial for maintaining optimal cognitive function, especially when it comes to executive functions. Glutamate is both an essential neurotransmitter and a neurotoxin, so achieving the right balance is essential.
Here are some natural strategies to help you achieve that balance:
Diet and Precursors:
Glutamine: This amino acid is a precursor to glutamate. You can find it in supplement form or naturally in foods like meat, fish, eggs, dairy, wheat, and certain vegetables.
Taurine: Taurine, available as a supplement and found in meat and seafood, can alter both GABA and glutamate levels.
Theanine: Naturally present in tea and available as a supplement, theanine lowers glutamate activity while boosting GABA levels.
Stress Reduction:
Chronic stress can increase glutamate production. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or acupuncture.
Exercise:
Regular physical activity positively influences neurotransmitter levels, including glutamate. Aim for at least 30 minutes a day of exercise.
Avoid Excessive Stimulants:
Limit caffeine and other stimulants, as they can disrupt neurotransmitter balance.
Supplements and Lifestyle Choices:
Consider N-acetylcysteine (NAC), an antioxidant that may help regulate glutamate levels.
Ensure adequate intake of vitamin B6, magnesium, and zinc, which play roles in neurotransmitter balance.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA): GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate neural excitability. It plays a role in maintaining a balance between excitation and inhibition, which is essential for executive control.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a crucial neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in maintaining the balance between excitation and inhibition in the brain. As the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA helps promote relaxation, reduce stress, and improve overall brain function. Achieving a calm and clear mental state involves not only increasing GABA levels but also maintaining a balance among neurotransmitters. Striking a harmony between excitatory and inhibitory signals is essential for optimal brain function.
Here are some strategies to support GABA balance:
Diet and Precursors:
Stress Reduction:
Chronic stress negatively impacts GABA levels. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
Quality Sleep:
Prioritise restful sleep. During deep sleep, the brain restores neurotransmitter levels, including GABA.
Avoid Excessive Stimulants:
Limit caffeine and other stimulants, as they can disrupt neurotransmitter balance.
Serotonin (5-HT): Although often associated with mood regulation, serotonin also influences executive functions. It affects impulse control, emotional regulation, and decision-making.
Serotonin plays a crucial role in mood regulation, feelings of well-being, and cognitive function. Maintaining balanced serotonin levels is essential for optimal executive function.
Here are some science-backed tips to naturally increase serotonin:
Get Plenty of Sunlight and Vitamin D:
Sunlight exposure helps boost serotonin production. Spend time outdoors to soak up the sun and enhance your mood. If sunlight is scarce (especially during colder months), consider light therapy or vitamin D supplements.
Give and Receive Affective Touch:
Physical touch, such as hugging, cuddling, or supportive gestures, can increase serotonin levels. Building connections with others through touch positively influences mood and immunity while reducing stress.
Keep a Journal of Appreciation:
Regularly practicing appreciation helps your mind identify and appreciate positive aspects of life that you have created. This practice can lead to increased serotonin release and overall well-being.
Histamine: While less studied than other neurotransmitters, histamine may play a role in attention and cognitive processes. Its receptors are present in the prefrontal cortex.
Histamine, plays a multifaceted role in our daily biological functions. While it promotes wakefulness, controls satiety, and supports gut motility, an unregulated histamine response can lead to hypersensitivity reactions and contribute to neurological dysfunction.
Here are some strategies to balance histamine for better executive function:
Diet and Nutrients:
BodyBio Calm: Consider using BodyBio Calm, a supplement specifically designed to modulate the histamine response. It combines trace minerals, amino acids, and adrenal adaptogens to manage excess histamine levels and support natural modulators of histamine in the body.
Choline-Rich Foods: Include foods like egg yolks, soy, liver, and seeds that provide nutrients for acetylcholine synthesis. Acetylcholine helps regulate histamine release.
Stress Reduction:
Chronic stress can exacerbate histamine sensitivity. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
Sunlight Exposure:
Sunlight helps regulate histamine production. Spend time outdoors to enhance mood and overall well-being.
Avoid Excessive Stimulants:
Limit caffeine and other stimulants, as they can disrupt neurotransmitter balance, including histamine.
As you can see - there are commonalities for all executive function neurotransmitters and supporting them to function properly and in balance.
In a nutshell we can all -
Get more natural light
Exercise
Eat a balanced diet
Reduce stress
Avoid excessive stimulants
Improve sleep patterns
If we do that then we are supporting executive function. This works for everyone. Especially children. We all need to be more autonomous and less passive when it comes to brain health. When the brain is unhealthy, we are really unwell. it really is as simple as that.
“Brain wave tests prove that when we use positive words, our ‘feel good’ hormones flow. Positive self-talk releases endorphins and serotonin in our brain, which then flow throughout our body, making us feel good. These neurotransmitters stop flowing when we use negative words.”